As a parent, you do everything in your power to ensure that your baby is healthy and well. There are numerous things that will keep you up at night during the first few months of your baby’s life, and the size of their head can be one of them.
The term macrocephaly may be used by your doctor, but should you be worried?
This post will explain what macrocephaly is and how to treat it. Read on to find more information about the causes, diagnosis, and treatment of macrocephaly in babies.
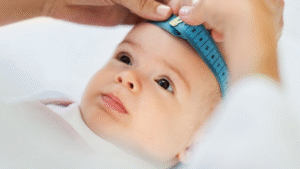
What is Macrocephaly?
Macrocephaly is a condition in which babies and children have an abnormally large head size. The condition is characterized by a head circumference that is larger than average for babies of the same age and sex.
Macrocephaly is generally diagnosed in babies whose head circumference is greater than the 97th percentile for their age and sex. In other words, only 3% of babies have a larger head circumference at any given age.
Head circumference can be measured during routine checkups or growth assessments performed by your pediatrician.
Causes of Macrocephaly
Macrocephaly can occur for a number of reasons. The condition is not always due to an underlying medical problem, and in many cases, it is completely harmless.
For example, some babies are simply born with a larger head circumference due to their genetic makeup and will not experience any health issues as a result.
However, in some cases, there can be an underlying cause for the condition that may require medical treatment or intervention.
Here are some of the most common causes of macrocephaly in babies:
1. Genetics
Genetics is one of the most common reasons why babies are born with a large head circumference or develop macrocephaly. It’s estimated that between 20% and 30% of children diagnosed with the condition have a parent who also has it.
Macrocephaly can run in families, and if a parent has a large head circumference, their child is more likely to have one as well.
Related: 7 Subtle Things That Can Affect Your Baby’s Appearance
2. Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a condition in which there is an accumulation of fluid in the brain. The excess fluid causes the head to swell and can result in macrocephaly.
Hydrocephalus can occur at birth or later during infancy. The condition requires immediate treatment as it can lead to serious complications if left untreated.
Congenital hydrocephalus is present at birth and can be caused by genetic defects or issues that occur during pregnancy.
Acquired hydrocephalus can develop after birth as a result of infections, bleeding in the brain, or head injuries.
In babies with hydrocephalus, the build-up of fluid in the brain can cause cognitive and developmental delays.
3. Benign Familial Macrocephaly
Benign familial macrocephaly is a type of macrocephaly that is passed down through families. Children with benign familial macrocephaly tend to have a larger head circumference, but they will usually grow and develop normally without any signs of disease.
4. Achondroplasia
Achondroplasia is a form of dwarfism, and babies with the condition may have an abnormally large head. The condition is caused by abnormal bone growth.
Babies with achondroplasia tend to have an abnormally large head size, but they will also often have short limbs and other characteristic features of the condition.
In addition to macrocephaly, babies with achondroplasia may also experience developmental delays.
Related:5 Non-Obvious Signs That Your Child May Be Ahead in terms of Development
5. Brain Tumors or Abnormal Growths
Brain tumors or abnormal growths can sometimes cause an increase in head size. Tumors in the brain can cause the skull to expand, leading to macrocephaly.
Brain tumors are a serious condition and require immediate diagnosis and treatment.
6. Subdural Hematoma
A subdural hematoma is a condition that occurs when there is bleeding between the brain and the skull. The bleeding can cause the head to swell and increase in size.
A subdural hematoma may be the result of a traumatic birth or injury to the baby’s head.
If left untreated, a subdural hematoma can cause neurological damage.
7. Metabolic Disorders
Metabolic disorders such as mucopolysaccharidoses (MPS) can also lead to abnormal head growth in babies.
MPS is a group of inherited conditions that affect the body’s ability to break down certain substances. This causes a buildup of these substances in the body and can lead to a range of physical and cognitive problems, including macrocephaly.
Related:Crying During Pregnancy: This Is How It Affects the Baby
How is Macrocephaly Diagnosed?
If a doctor suspects that a baby has macrocephaly, they will usually perform a thorough assessment. This can include:
1. Measuring the Baby’s Head Circumference
The doctor will take a measurement of the baby’s head circumference and compare it to a growth chart to see if the head is larger than it should be for the baby’s age and sex.
2. Physical Examination
The doctor will perform a physical examination to check the baby’s overall development. They will look for any other signs or symptoms of a medical condition that could be causing macrocephaly.
3. Imaging Tests
If a doctor suspects that there is an underlying condition causing macrocephaly, they may order an imaging test such as an ultrasound, MRI, or CT scan to take a closer look at the baby’s brain.
Ultrasounds are often used for infants under six months of age, while MRI or CT scans may be used for older babies.
4. Blood Tests
In some cases, blood tests may be done to look for underlying metabolic or genetic disorders that could be causing macrocephaly.
5. Neurological Assessment
If there are any concerns about developmental delays, the doctor may perform a neurological assessment. This can include testing the baby’s reflexes, muscle tone, coordination, and response to different stimuli.
This can help the doctor understand how well the baby’s brain and nervous system are working.
Related:What Your Baby’s Birth Weight Tells You
Treatment Options for Macrocephaly
The treatment for macrocephaly will depend on the underlying cause. In many cases, treatment is not required, and the condition will resolve on its own over time.
If there is an underlying medical condition causing macrocephaly, treatment will be necessary to address it.
In some cases, surgery may be required to treat macrocephaly. For example, if the condition is caused by hydrocephalus, surgery may be necessary to drain the excess fluid from the brain and relieve pressure.
Other treatment options for macrocephaly include:
1. Observation
In many cases, where macrocephaly is caused by benign or familial reasons, the doctor may simply monitor the baby’s head growth over time. No medical intervention is required in these cases.
2. Surgical Treatment for Hydrocephalus
Surgery may be necessary to drain the excess cerebrospinal fluid and relieve pressure on the brain. A shunt, which is a small tube, is usually inserted to help drain the fluid from the brain and prevent further complications.
3. Gene Therapy and Support for Metabolic Disorders
Treatment for babies with metabolic disorders will focus on managing symptoms and using therapies that are designed to help the body break down accumulated substances. Gene therapy and enzyme replacement therapies are still in their early stages and are not yet widely available.
4. Tumor Removal
Surgery may be required to remove a brain tumor or abnormal growth that is causing macrocephaly. In some cases, additional treatments such as chemotherapy or radiation may be needed, depending on the nature of the tumor.
5. Physical Therapy
Physical therapy and other interventions may be necessary to help with motor delays and improve mobility for babies with achondroplasia.
Specialized therapies can help improve muscle strength and coordination, improving the baby’s development.
Related:25 food That Will Increase Your Baby’s Brain Power
When Should You Worry?
Macrocephaly is not usually a cause for concern, but there are a few signs that may indicate an underlying medical problem. These include:
Rapid Increase in Head Size: If the baby’s head is growing rapidly over a short period of time, it could be a sign of a more serious condition, such as hydrocephalus.
Developmental Delays: If the baby is not hitting their developmental milestones at the expected times, it could be a sign of an underlying medical problem.
Signs of Brain Pressure: If the baby is showing signs of irritability, vomiting, seizures, or lethargy, these could be signs of increased pressure in the brain and require immediate medical attention.
Conclusion
Macrocephaly in babies is a condition that should not cause concern in most cases. In fact, in the majority of cases, macrocephaly is harmless and is simply a result of your child’s genetic makeup.
Macrocephaly can, however, sometimes be a sign of an underlying condition, and it is important to keep a close eye on your child’s development. If you are concerned about your baby’s head size, it is important to speak to your doctor so that they can assess the situation and provide you with guidance and reassurance.
With regular checkups and growth assessments, your pediatrician will be able to track your baby’s development and catch any issues before they become a problem. If your baby has macrocephaly, trust your doctor and know that you are doing everything you can to keep your little one healthy.
Save the pin for later

- 8th Month Pregnancy Care: What To Expect, Dos And Don’ts - January 17, 2026
- 80 Beautiful Hispanic Girl Names for Your Baby - January 8, 2026
- 7 Physical Signs Your Baby Still Isn’t Ready to Come Out - November 28, 2025